Very often when we approach to the world of golden retriever we hear of hip dysplasia, but what is?
Hip Dysplasia is an abnormal development of the articulation between femur and pelvis (hip). Mainly affects the medium-large sized dogs but rarely can also affect small dogs and cats.
It should be noted that the congenital dysplasia is a genetic disease and not congenital, this is a mistake that you make when it comes to this problem: a genetic disease is when the puppy is transmitted by parents through their dna (genes), a disease is congenital when present and manifest since birth.
Then a Dysplastic pup is genetically predisposed to the disease but at birth is not sick; its components are currently normal bone despite genetic predisposition, which is necessary for the development of the disease. Hip Dysplasia is considered to be a multifactorial etiology, pathology but the hereditary component, therefore, seems to be predominant.
Multifactorial etiology is a disease that is caused by several factors. The factors involved are genetic, nutritional, environmental, physiological, biomechanical and structural, and everyone plays a role more or less influential in the pathogenesis of dysplasia and aggravate laxity leading to joint incongruity and osteoarthritis. However, it is well established that environmental factors, without a genetic basis, cannot determine the development of the disease.
Predisposing factors:
- Fast growing
- Overweight puppies
- Traumas (jumps, slips, sprains, stairs)
- Unhealthy diet
- Excessive exercise
Hip Dysplasia occurs between 4 and 12 months of age, but most often around 7 8 months, although less severe forms can be highlighted even belatedly.
Symptoms
The predominant symptom is the lameness, more or less serious. However, except in very severe cases, there is no event before seven eight months old. In young dogs dysplasia can manifest with a tendency to sit often (exercise intolerance) and Gallop like a "rabbit" with the hind legs parallel and joined.
Diagnosis
It is very important to have a diagnosis as soon as possible to safeguard the health of the dog and minimize the development of arthritis which is a leading cause of pain in this disease. Early diagnosis can be made already at 5 months of age through a thorough orthopedic veterinary visit which also includes a radiographic study,
It is very important that the radiographic study and a part of the visit are taken under sedation in order to really evaluate orthopaedic joint laxity and angles and subluxation reduction, this is not possible when the dog is awake because of muscle contraction.
It is often thought that for a puppy so small the sedation is too "heavy" or "not worth" to sedate him for radiographs, actually are proposed at this age because, in case of severe Dysplasia, there are certain health surgeries which can only within certain age limits.
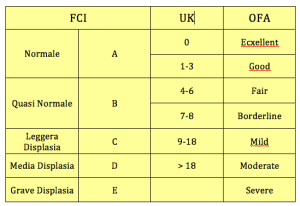
Dysplasia is classified into 5 grades from A to E, where A indicates perfect and E severe dysplasia.
Therapy
Treatment of hip dysplasia follows two main streets: surgical and medical therapy. Medical therapy can be made for mild cases and pending the possible surgery and is based on the use of drugs, monitoring of physical activity and dietary supplements that decrease joint damage.
Surgical therapy open various possibilities in relation to the age of the dog. In very young subjects (within 5 months of age) can be made pubic sinfisiodesi surgery (non-invasive and with good prognosis) which provides for the closure of the physis pubic growth (pelvis), resulting in a rotation of the pelvis, which in turn leads to better shape the joints of the hips.
At older ages (within seven and a half months) you can make a double pelvic osteotomy (dpo) which consists of cutting and repositioning pelvic bones using screws and plates. In adults there are only two types of surgery: resection of the head and neck of the femur and the hip. The femoral head and neck resection involves the removal of the head and neck of the femur of the affected joint thus eliminating the pain.
Generally the subject will present anyway lameness although mechanically without the presence of pain. This surgery is not recommended for dogs with a greater weight of 20/25 kg. The hip replacement surgery is an operation that covers the replacement of the joint components with teflon and metal implants. Corrective action with complications sometimes important.
Being a pathology with hip dysplasia hereditary basis is absolutely recommendable the exclusion of subjects suffering of dysplasia from the reproduction.





Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.